In the field of safety at work, choosing the right shoes is essential to protect firefighters from risks associated with their interventions.
Let's explore the differences between EN 15090, EN ISO 20345 and EN ISO 20347 standards regarding work shoes.
standard EN 15090
The EN 15090 standard is specific to firefighter boots and shoes. It defines all the performance requirements for footwear worn by firefighters to face fires.
These shoes must provide protection against heat, flame, as well as adequate grip on different types of ground
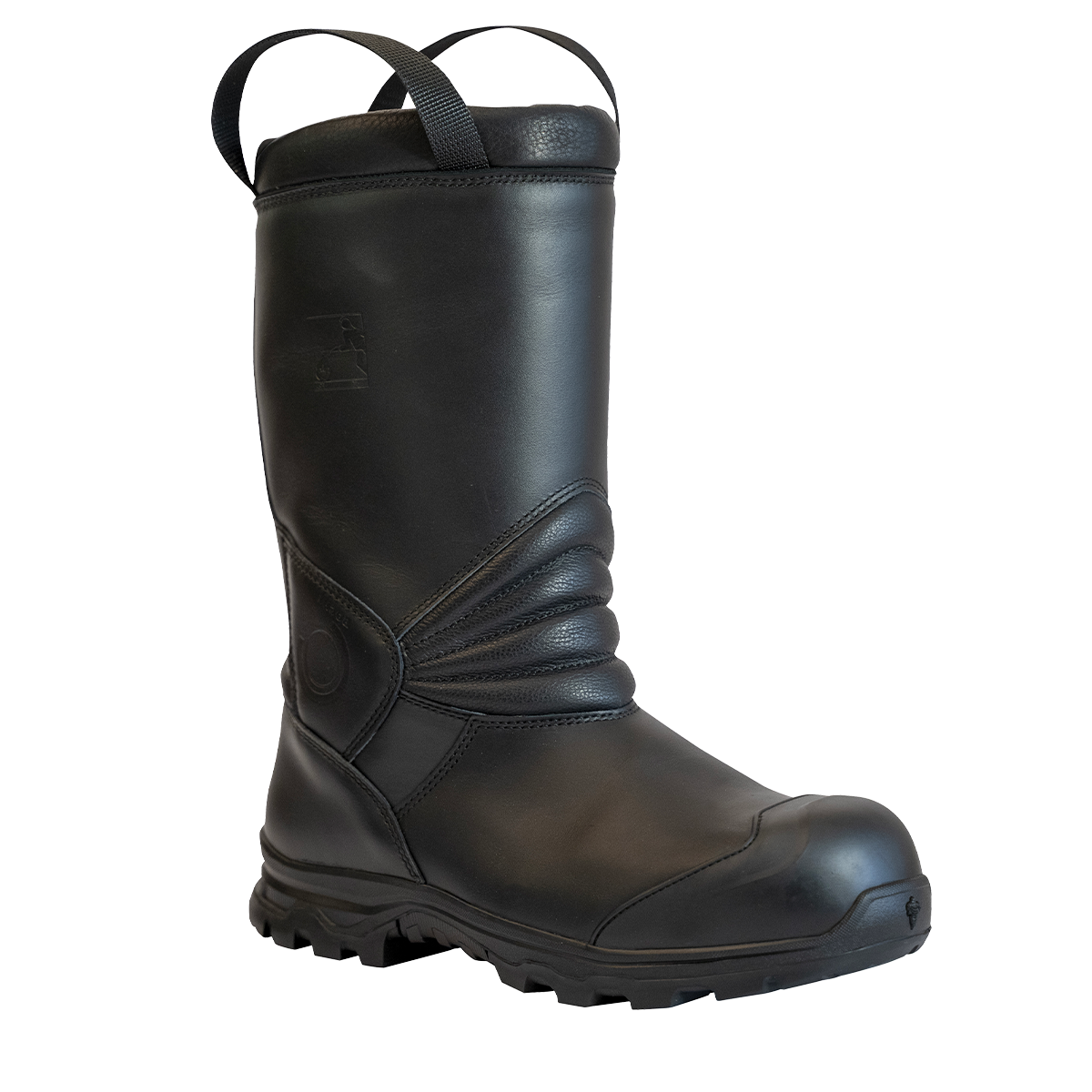
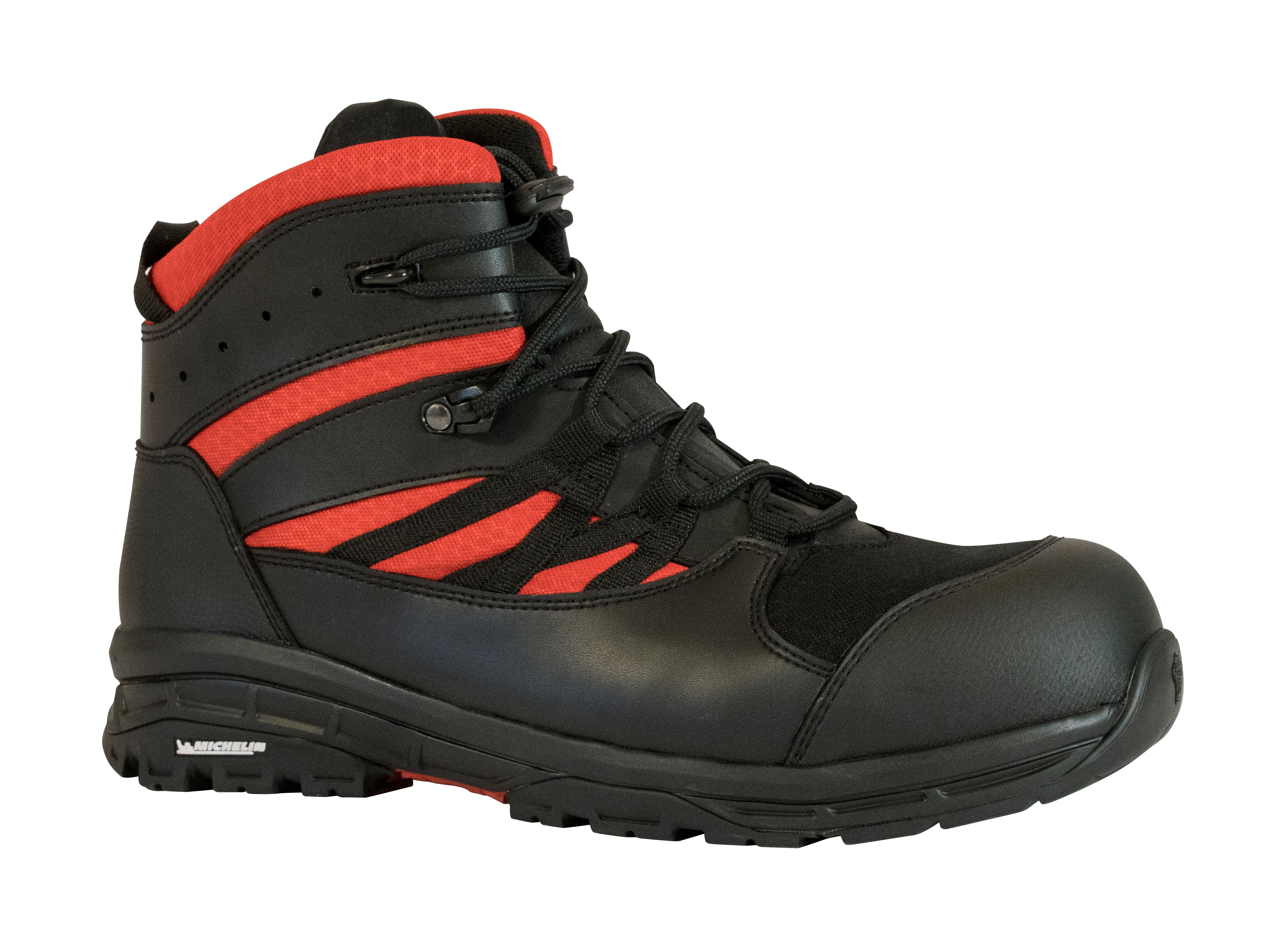


Standard EN ISO 20345
EN ISO 20345 is the basic standard for safety footwear. It specifies the minimum requirements level for personal protective footwear in industry. Footwear in compliance with this standard must provide protection against impact stubbed toes, as well as resistance to puncture and slipping.
You can also check out our Type A EOLE and MERCURE models or our boots B2 CS available on our catalog.
Our BOCHE’s R4AE meet this standard and is particularly suitable for Young Firefighters (JSP).
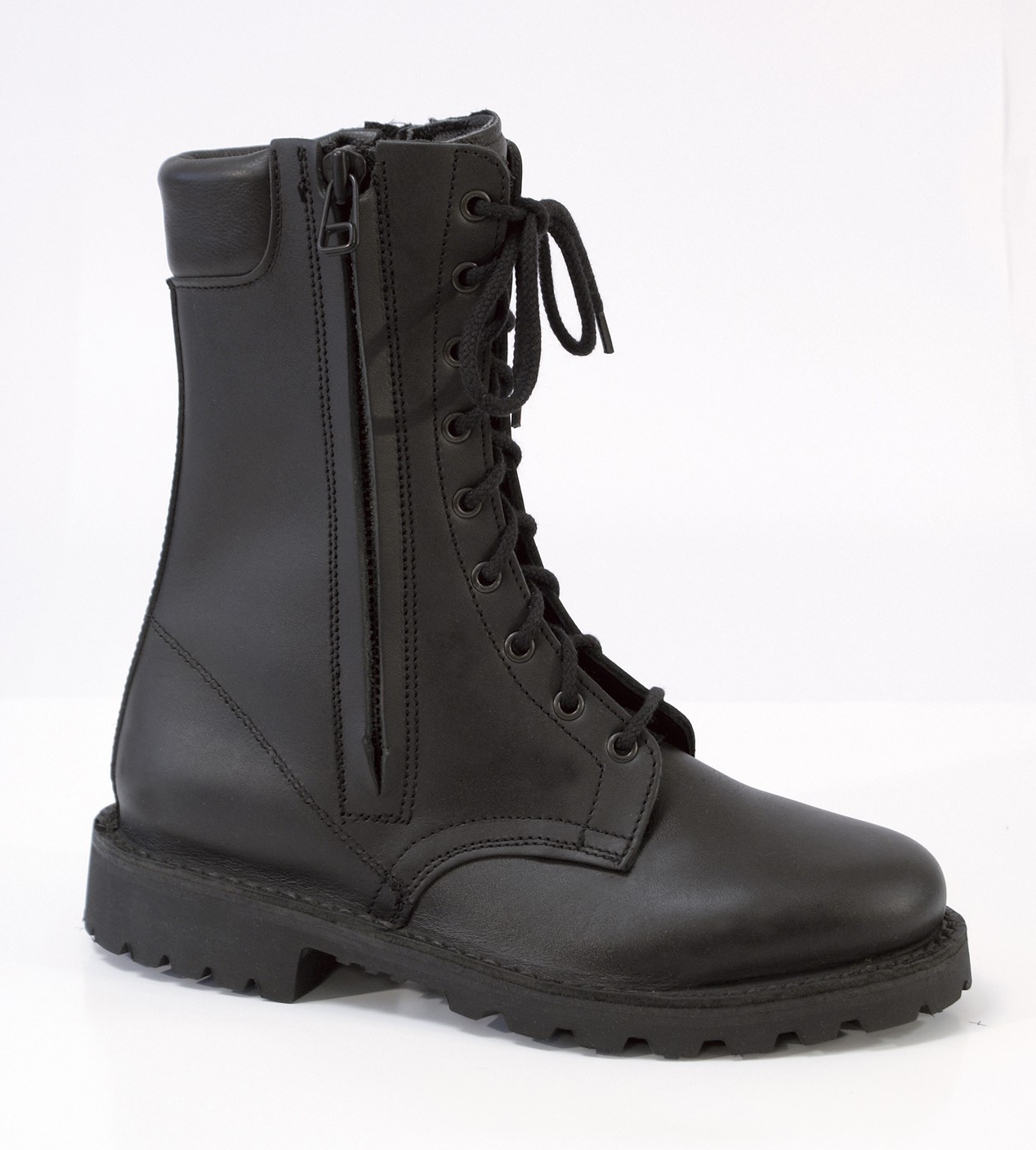
Standard EN ISO 20347
The EN ISO 20347 standard regards occupational footwear without toe protection. It applies to shoes used in environments where the risk of foot injuries is lower without handling heavy loads.
Our models, however, have a sole resistant to contact heat (> 300°C).
At BOCHE, our models B3 HIP, R22P, NASA N, R23 PN (available on pages 20 and 21 in our catalog) meet this standard.

Understanding European footwear standards is crucial to guarantee firefighters safety in their different operating environments.
By knowing the differences between EN 15090, EN ISO 20345 and EN ISO 20347 standards, Heads of Equipment Department can select the perfect model adapted to the specific needs of their staff.
Investing in quality footwear that meets appropriate standards helps to reduce the risk of injury and ensure a safe working environment.